
Generally, the majority of value investors will NOT invest in a security unless the MOS is calculated to be around ~20-30%. Instead of shorting stocks or purchasing put options as a hedge against their portfolio, a large proportion of value investors view the MOS concept and long holding periods as the most effective approach to mitigating investment risk.Ĭoupled with a longer holding period, the investor can better withstand any volatility in market pricing. if the share price were to decline substantially post-purchase. What is the Role of Margin of Safety in Value Investing?įrom a risk standpoint, the margin of safety serves as a buffer built into their investment decision-making to protect them against overpaying for an asset - i.e. In this particular example, the MOS is 25% - meaning that the share price can drop by 25% before reaching the estimated intrinsic value of $8. Suppose a company’s shares are trading at $10, but an investor has estimated the intrinsic value at $8. Intrinsic Value → The implied value of a company’s equity on a per share based on the fundamentals of the issuer.

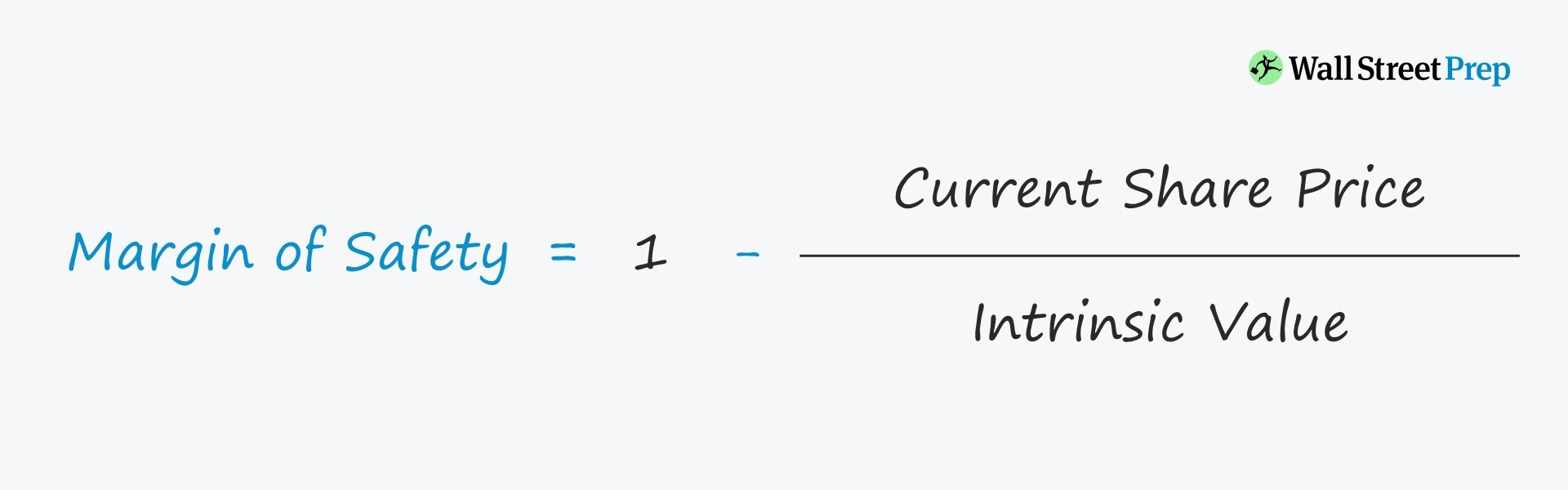
Current Share Price → The share price of the company’s stock on the present date.Margin of Safety (MOS) = 1 − (Current Share Price ÷ Intrinsic Value) To estimate the margin of safety in percentage form, the following formula can be used. In other words, purchasing assets at discount decreases the negative effects of any declines in value (and reduces the chance of overpaying). Therefore, the margin of safety is a “cushion” allowing for some degree of losses to be incurred without suffering any major implications on returns.

The margin of safety (MOS) is one of the fundamental principles in value investing, where securities are purchased only if their share price is currently trading below their approximated intrinsic value.Ĭonceptually, the margin of safety could be thought of as the difference between the estimated intrinsic value and the current share price.īy only investing if there is sufficient “room for error”, an investor’s downside is more protected. The Margin of Safety represents the downside risk protection afforded to an investor when the security is purchased significantly below its intrinsic value.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
